Europe’s Natural Gas Storage Inventories at All-Time High Due to Mild Winter, Demand Reduction Measures: EIA
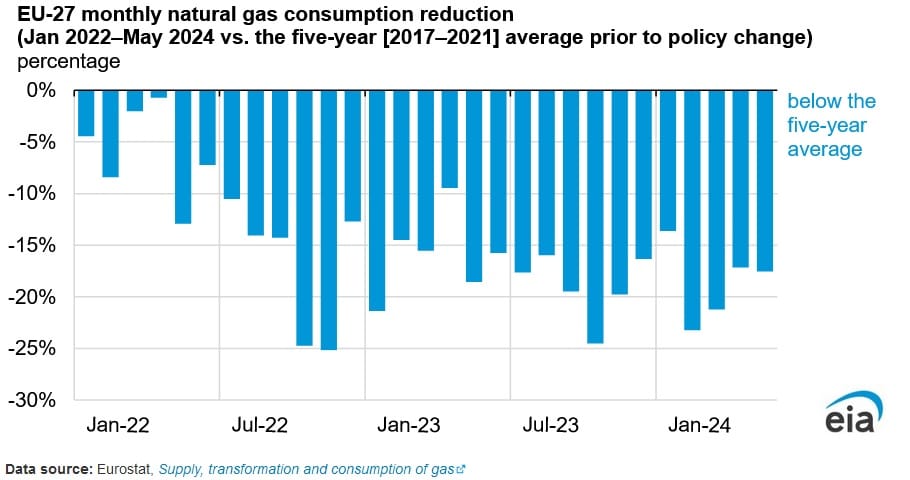
European natural gas usage has been on a downward trend since mid-2022, according to a July 23 report published by the U.S. Energy Information Administration. The decline in natural gas usage can be attributed to lower demand due to milder winters and government policies directed at reducing gas usage.
Natural gas usage across Europe declined 18 percent during 2023 compared to the previous five-year average (2017-2021). Moreover, consumption declined 19 percent during the January-May 2024 period, compared to the average of the same period between 2017 and 2021.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 led to a reduction in the amount of Russian pipelined gas coming towards Europe. In order to ensure gas supply in the domestic market is sufficient to fulfil domestic demand, European governments, in coordination, enacted demand reduction policies and measures. These policies directed a minimum 15 percent reduction in natural gas usage from August 2022 to March 2023. These policies were further extended up until March 2025.
The Netherlands, France, Italy, and Germany account for around two thirds of the gas consumption across Europe. The reduction in these countries accounted for a total 5 billion cubic feet per day (Bcf/d) during 2023 and 6 Bcf/d during the first five months of 2024, compared to the five-year average during 2017-2021, before the implementation of government policies. Since the demand reduction policy deployment, the 10 top gas consuming countries in Europe have seen consumption decline between 1 to 28 percent.
Two consecutive mild winters during 2022–23 and 2023–24 coupled with lower gas consumption due to both government policies and higher renewable generation led to record high end of heating season storage stocks in both 2023 and 2024. Gas storage sites were recorded at 59 percent full across Europe, as of April 1, 2024. This was the highest level on record for the end of the heating season.
European natural gas pipeline imports from Russia declined by 58 percent during 2022 and 89 percent in 2023, compared to the 2021 yearly average. The Russian invasion of Ukraine, has led to a shift in global trading dynamics and increased the European markets reliance on U.S. Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) to fulfil domestic demand.
EnerKnol Pulses like this one are powered by the EnerKnol Platform—the first comprehensive database for real-time energy policy tracking. Sign up for a free trial below for access to key regulatory data and deep industry insights across the energy spectrum.
ACCESS FREE TRIAL