California’s Greenhouse Gas Emissions Dropped 20 Percent From 2000-2022: CARB
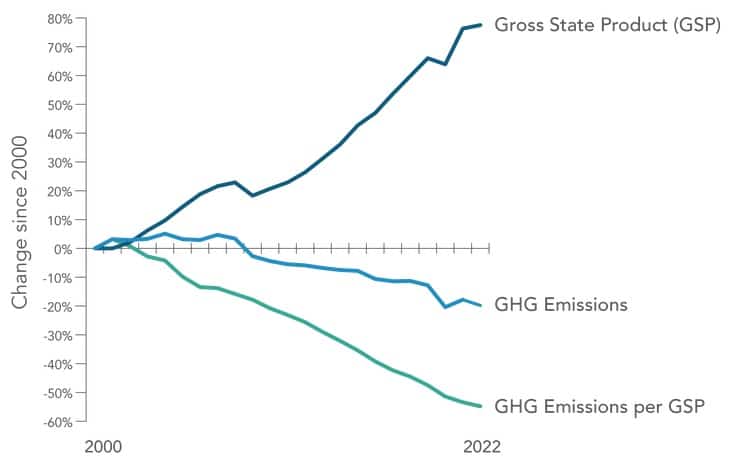
The California Air Resources Board released a report presenting data on greenhouse gas emissions in 2022, highlighting a consistent decline in emissions alongside economic growth. From 2000 to 2022, emissions dropped by 20 percent while California’s gross domestic product rose by 78 percent. The carbon intensity of the state’s economy has also decreased by 55 percent in the last two decades, according to the report.
California has a statutory goal of reducing emissions at least 85 percent below 1990 levels by 2045. Additionally, utilities are required to obtain 60 percent of retail sales from renewable sources by 2030 and 100 percent from carbon-free resources by 2045.
In 2022, statewide greenhouse gas emissions were 371.1 million metric tons, a 2.4 percent decrease from 2021 levels. The largest decline in emissions came from the transportation sector, stemming from greater use of renewable and alternative fuels as well as a steady increase in the use of electric vehicles.
California has been investing heavily in programs to incentivize the use of electric vehicles and developing the necessary electric vehicle infrastructure, which has contributed to the steep increase in zero-emission vehicles on the road. This month, California announced an allocation of $500 million toward electrifying school bus fleets across the state. During the first quarter of 2024, sales of ZEVs surpassed 100,000, putting California ahead of its sales targets for ZEVs. Further, stricter regulations such as the Low Carbon Fuel Standard and Advanced Clean Cars supported emissions reductions in the transportation sector.
The electricity sector saw its lowest carbon intensity since 2000. This sector’s emissions reduction is attributed to the larger share of renewable sources involved in California’s electricity generation. Wind and solar power now account for 30 percent of electricity production in the state. Solar power showed a 15 percent increase from the previous year, owing to the state’s Cap-and-Trade Program and Renewables Portfolio Standard.
In addition to renewable power generation, California has also invested in efforts to improve battery storage systems. Between 2019 and 2023, battery storage capacity increased by 757 percent, capable of powering more than 6.6 million households for four hours.
California’s agricultural sector also recorded a decrease in emissions, particularly from livestock which accounts for 70 percent of GHG emissions in California. The Low Carbon Fuel Standard supported the use of methane digesters through the California Climate Investments. These digesters reduce methane emissions by capturing methane released from livestock and converting it into clean fuel.
EnerKnol Pulses like this one are powered by the EnerKnol Platform—the first comprehensive database for real-time energy policy tracking. Sign up for a free trial below for access to key regulatory data and deep industry insights across the energy spectrum.
ACCESS FREE TRIAL