Texas Electricity Grid Experiences Record High Demand During Recent Heat Wave: EIA
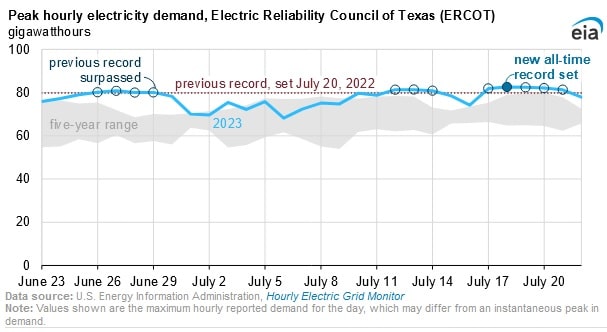
Power demand in Texas hit record highs in late June and July as homes and businesses increased air conditioning, fans, and other cooling equipment to tackle extreme heat waves. Hourly demand on the Texas power grid peaked at 82,579 megawatthours on July 18 in the 6:00 p.m. hour central time, according to a July 26 report from the U.S. Energy Information Administration. The Electric Reliability Council of Texas, which manages power flow to more than 26 million Texas customers representing about 90 percent of the state’s electric load, has in recent times increased output significantly to meet the soaring demand.
ERCOT’s record for hourly demand has consistently been broken over June and July, with the previous record for hourly demand being 79,830 MWh on July 20, 2022. This record was broken daily from June 26 to June 29 this year, with the highest demand for each of those days being more than 80,000 MWh. Moreover, demand broke new records on July 12, 23 and 17 before peaking on July 18.
Natural gas was the common energy source of electricity production in most record high generation hours. Non fossil fuels consisting of wind, solar and nuclear also contributed notably (55 percent of total generation) during the high demand days of June 28 and June 29. This is in contrast to previous periods of high demand (August 2019 and August 2022) where non-fossil fuel electricity generation never reached more than 50 percent of the total production in ERCOT.
The wholesale electricity price increase due to record high demand was lower than expected and below the price levels experienced in previous heat waves in August 2019 and August 2022. In August 2019, day-ahead prices in the grid operator’s Houston zone averaged $172/MWh during daylight hours and $112/MWh in August 2022. In comparison, these prices during the recent heat wave were at $79/MWh. Wind and solar generation have zero fuel costs and nuclear and hydropower plants only have low variable operation costs that are not incorporated in their bids to generate wholesale electricity. The increase in renewable generation and lower gas prices compared with last summer were key drivers during the most recent heatwave.
The generation blend in ERCOT has swiftly changed in recent years, with 4,000 megawatts of wind and solar included between September 2022 and May 2023. As a result of an increase in intermittent generation, ERCOT have announced a new daily procured ancillary service aimed to support grid reliability and reduce real-time operational issues to balance supply and demand.
EnerKnol Pulses like this one are powered by the EnerKnol Platform—the first comprehensive database for real-time energy policy tracking. Sign up for a free trial below for access to key regulatory data and deep industry insights across the energy spectrum.
ACCESS FREE TRIAL