U.S. Electricity Generating Capacity Retirements Expected to Decrease by Over 60 Percent This Year: EIA
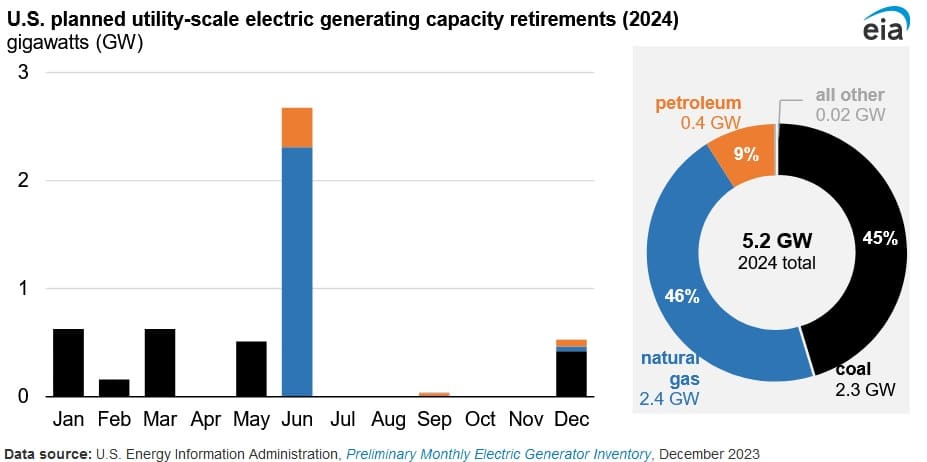
The U.S. is projected to retire 5.2 gigawatts (GW) of electricity generating capacity in 2024, according to a Feb. 20 report published by the U.S. Energy Information Administration. The expected retirement of power generating capacity this year is 62 percent lower than 2023 and is the lowest yearly decline since 2008. Coal and natural gas together account for 91 percent of planned generating capacity retirements in 2024.
U.S. coal fired power generating capacity retirement is expected to slow down in 2024, with the 2.3 GW of scheduled retirement representing 1.3 percent of the country’s coal fleet. By comparison, 22.3 GW of coal fired capacity retired during the previous two years. Coal capacity retirements are projected to increase again during 2025, when asset owners expect to close around 10.9 GW of capacity. According to the agency, older units are expected to account for a large share of coal plant closures during 2024. The retiring units have a capacity weighted average age of 54 years, which is about 10 years higher than that of operating coal units. Coal fired generating assets have been facing intense competition from natural gas and renewables, as a result these assets have been vastly expensive to operate. Moreover, the structural change in the market as a result of legislation and the increasing demand for solar and battery storage has led to coal being less favourable in the electricity generation mix.
U.S. gas fired electric generating capacity planned to retire during 2024 is projected to be 2.4 GW and accounts for 46 percent of total U.S. capacity retirements. This represents around 0.5 percent of current operational U.S. gas fired capability. The Mystic Generating Station, which has the capacity to produce 1.41 GW of electricity is expected to account for around 60 percent of the natural gas fired capacity retirements in 2024. The remaining retirement capacity is projected to come from the Tennessee Valley Authority Johnsonville station.
EnerKnol Pulses like this one are powered by the EnerKnol Platform—the first comprehensive database for real-time energy policy tracking. Sign up for a free trial below for access to key regulatory data and deep industry insights across the energy spectrum.
ACCESS FREE TRIAL