Visual Primer: Carbon Market Developments Drive Momentum for U.S. Climate Policy
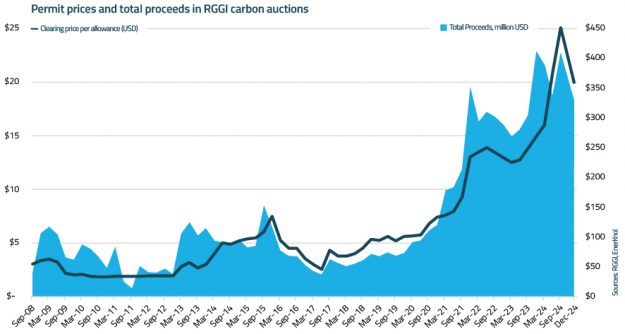
U.S. carbon markets are experiencing a resurgence as key states reinforce their commitment to cap-and-trade systems despite hurdles. Washington's latest carbon auction saw prices rebound following voter support for its program, while a court ruling has invalidated the controversial withdrawal of Virginia from the regional carbon market. Meanwhile, progress in California, Québec, and Washington toward potential program linkage signals a move toward greater market integration, setting the stage for more robust and scalable climate solutions nationwide.