Visual Primer: Rising Electricity Demand Spurs Efforts to Improve Interconnection Efficiency
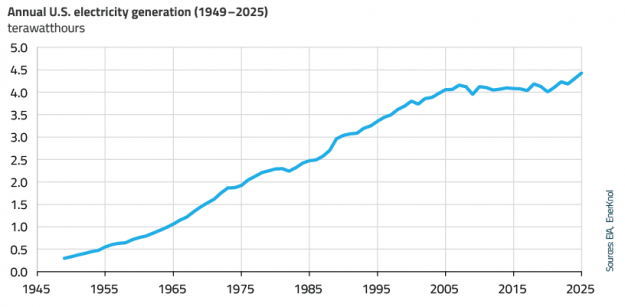
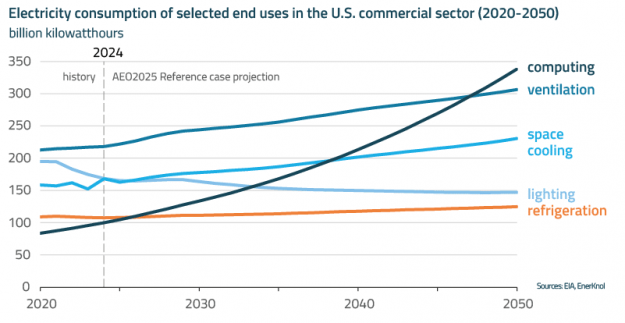
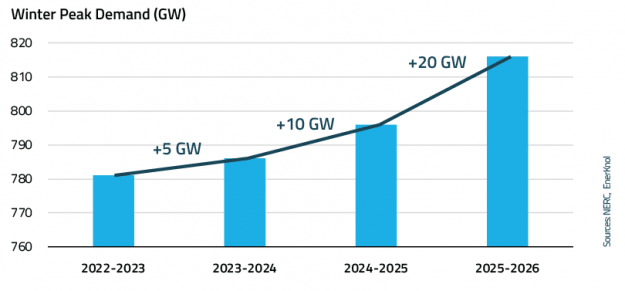
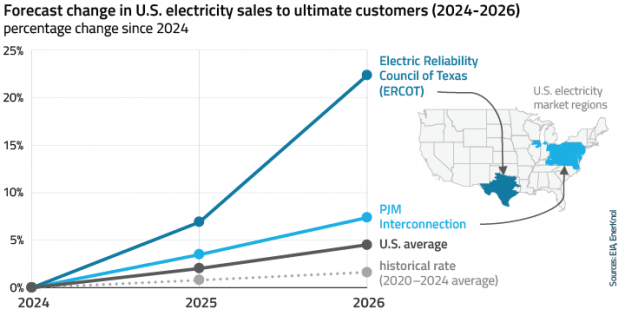
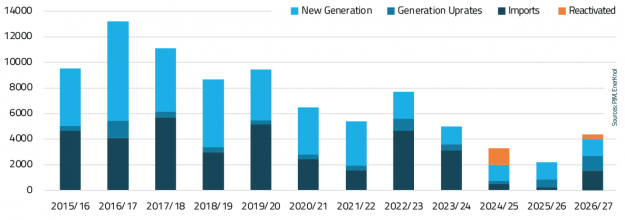
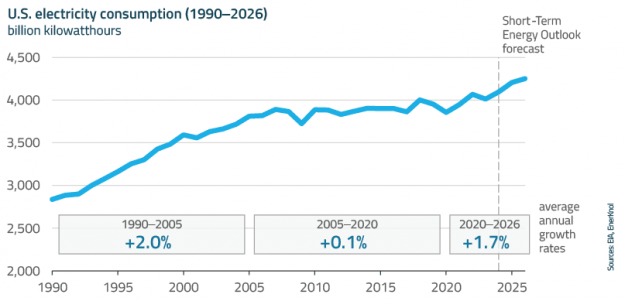
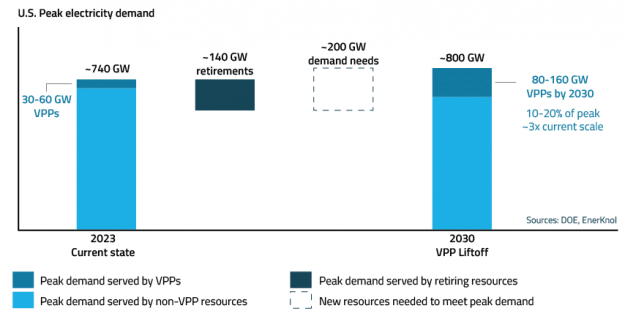
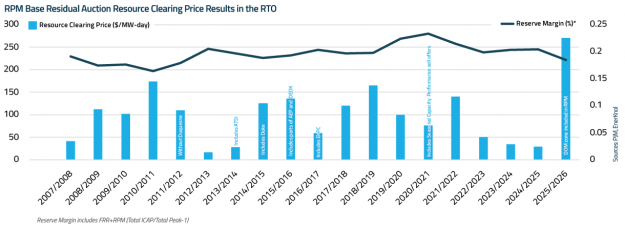
Regulators and grid operators across the U.S. are actively reforming interconnection processes to support the growth of new power generation resources amid surging electricity demand from AI data centers, manufacturing, and electrification. These actions also aim to address emerging challenges arising from the rapid growth of new large loads, which can introduce planning uncertainty and require substantial investments in transmission and other grid infrastructure.