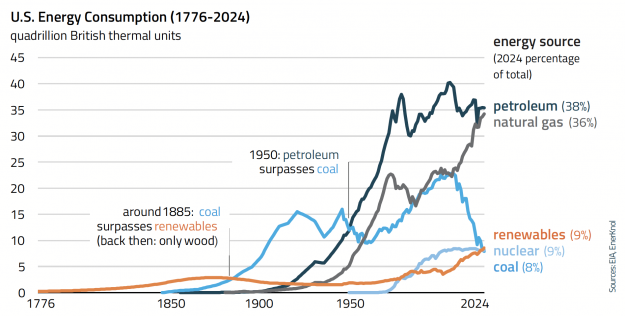
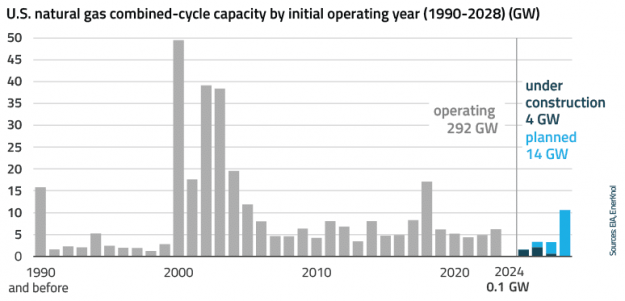
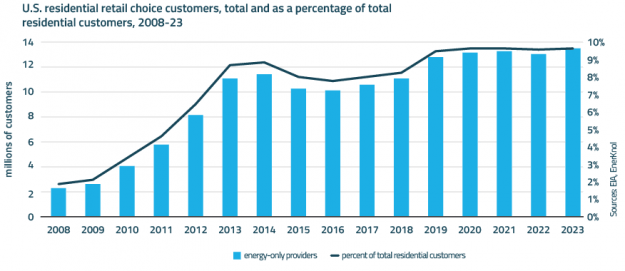
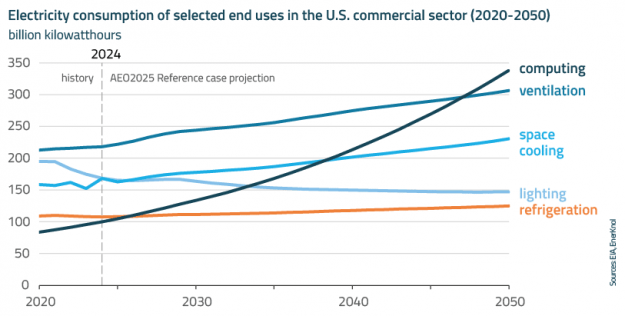
Visual Primer: ‘One Big Beautiful Bill’ Reinforces President Trump’s Fossil Fuel Agenda
U.S. President Donald Trump on July 4 signed the One Big Beautiful Bill Act, a sweeping reconciliation measure that fundamentally reshapes federal energy policy. The law dramatically shrinks the window for wind and solar projects to qualify for federal tax credits, and expands fossil fuel development on federal lands, reshaping the outlook for energy transition investments across the U.S.